Table of contents
Introduction
Put and Patch are both HTTP methods and basically, both are used to update or modify the data on the web server. While some people may think the methods are the same because the task methods are performing is the same, and yet there are some major differences between these two methods.
PUT Method
The PUT method is used to completely replace an existing resource with a new representation. It requires the client to send a complete representation of the resource in the request payload. When the server receives a PUT request, it replaces the entire resource at the specified URL with the new representation provided in the request payload. If the resource does not exist at the given URL, it may create a new resource.
PATCH Method
The PATCH method is used to partially update an existing resource. It allows the client to send only the changes or differences between the current representation of the resource and the desired updated representation. The server applies these changes to the resource, modifying only the specified fields or properties, while leaving the rest of the resource unchanged.
More Detailed View
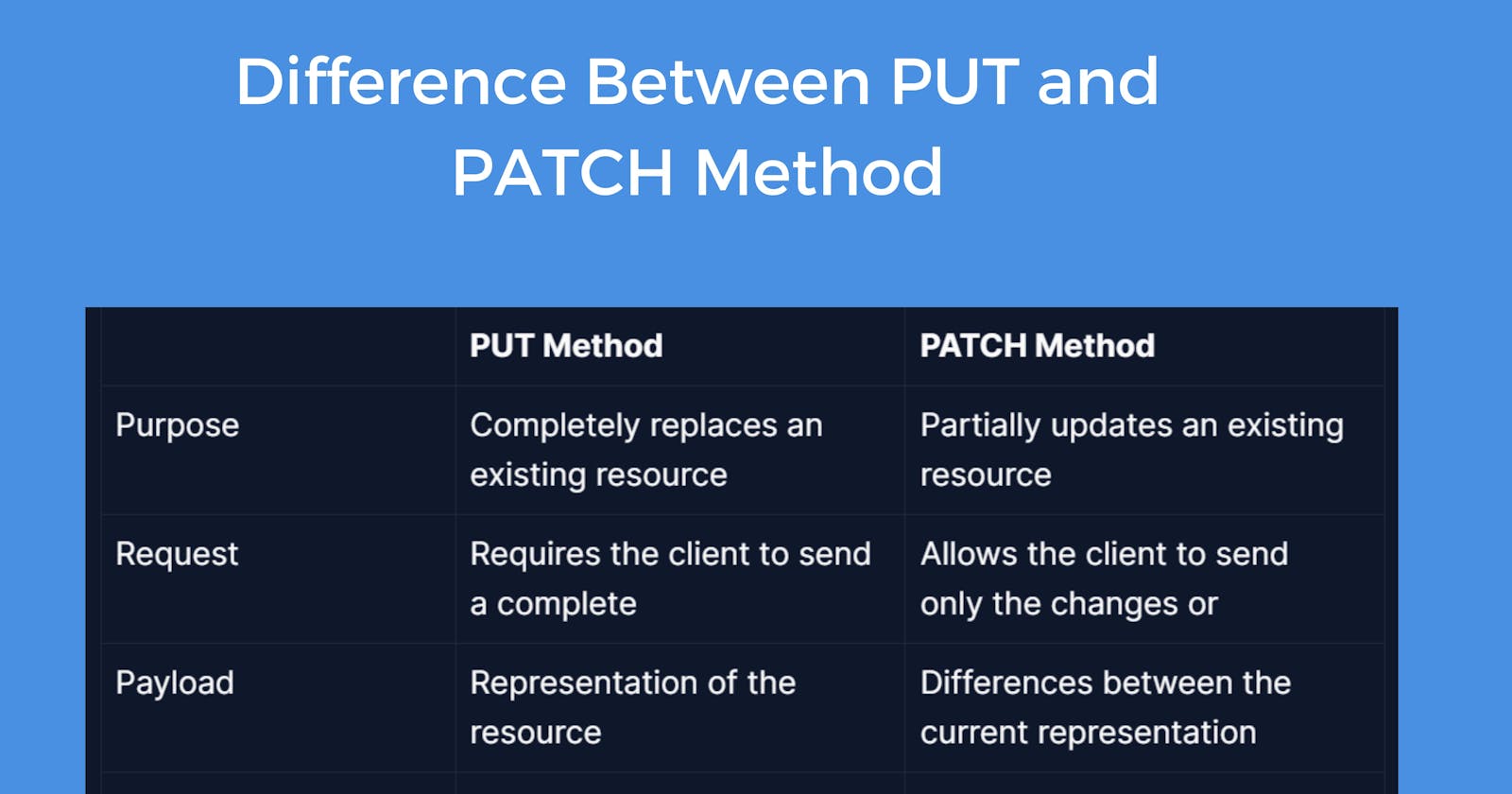
| PUT Method | PATCH Method | |
| Purpose | Completely replaces an existing resource | Partially updates an existing resource |
| Request | Requires the client to send a complete | Allows the client to send only the changes or |
| Payload | Representation of the resource | Differences between the current representation |
| Resource | Replaces the entire resource at the | Applies changes to the specified fields or |
| Error Handling | May result in unintended consequences if | Typically safer as it avoids overwriting |
Ending Note
Please keep in mind that the actual behavior and implementation of these methods can vary depending on the server or API framework being used. The above content represents the general differences and behavior of the PUT and PATCH methods.